Okay, let’s be real. When you hear whispers about the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) stepping in to manage the rupee’s exchange rate , it’s not just another headline. It’s a sign that things are getting interesting. And in the world of finance, “interesting” can mean opportunity, or it can mean potential turbulence. So, what’s really going on, and why should you care? That’s what we’re going to unpack here, focusing on the ‘why’ angle – why this matters to you, especially if you’re an Indian with a stake in, well, pretty much anything.
Why Rupee Intervention Matters | More Than Just a Number
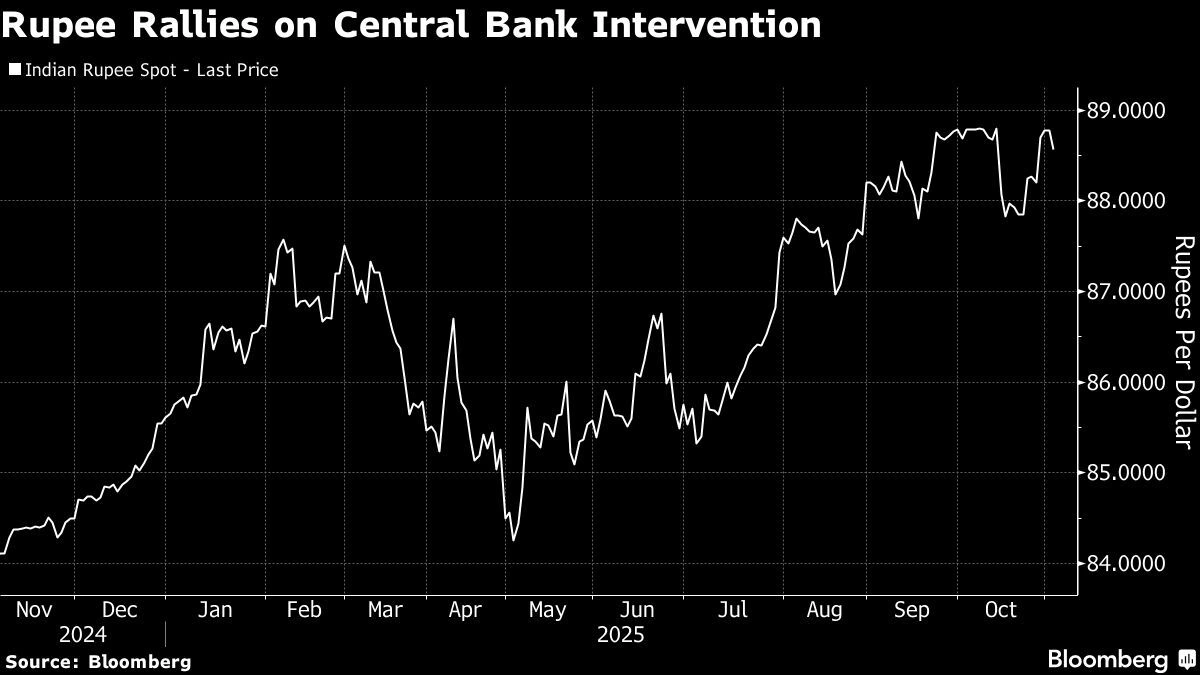
First, let’s ditch the jargon. Rupee intervention basically means the RBI is expected to buy or sell Indian rupees in the foreign exchange market. It’s like the central bank playing referee to keep the currency market from getting too wild. But why bother? Here’s the thing: a rapidly depreciating rupee can lead to imported inflation. Think about it India imports a lot, especially oil. A weaker rupee means those imports get more expensive, and those costs get passed on to you, the consumer. Petrol prices go up, your grocery bills increase, and suddenly your budget is feeling the squeeze.
And it’s not just about your wallet right now. A volatile rupee can spook investors. Nobody wants to put money into a country where the currency is all over the place. This can affect foreign investment, which in turn impacts economic growth. So, the RBI’s actions here are about more than just keeping the rupee at a certain level. It’s about maintaining stability and confidence in the Indian economy.
The Ripple Effect | Who Really Feels the Intervention?
So, who really feels the impact of a rupee intervention ? Well, pretty much everyone, but in different ways. For exporters, a weaker rupee can actually be good news. It makes their goods cheaper and more competitive in the global market. But importers? Not so much. They’re facing higher costs, which can eat into their profits or force them to raise prices.
What about the average person? As we touched upon, a weaker rupee can lead to inflation, impacting household budgets. But a stable rupee, managed effectively by the RBI, can help keep inflation in check. And here’s the slightly quirky part – the timing of these interventions matters a lot. The RBI typically intervenes before market opens to signal its intent and to try and prevent panic or excessive speculation. It’s like a preemptive strike to calm the market’s nerves. I initially thought this was straightforward, but then I realised the scale of the impact. When rupee plummets , the response can be significant.
The Toolkit | How Does the RBI Actually Intervene?
Alright, so how does the RBI actually pull this off? It’s not like they just snap their fingers and the rupee magically stabilizes. The main tool in their arsenal is buying or selling foreign currency reserves, primarily US dollars. If the rupee is weakening, the RBI might sell dollars and buy rupees. This increases the demand for rupees, which can help strengthen its value.
Conversely, if the rupee is getting too strong (which is less common but can still happen), the RBI might buy dollars and sell rupees. This increases the supply of rupees, which can help moderate its rise. According to data from the RBI website , these interventions are carefully calibrated based on market conditions and the overall economic outlook.
Challenges and Considerations | It’s Not a Perfect Science
Now, let’s be honest: currency intervention isn’t a foolproof solution. There are limits to what the RBI can achieve. If global factors are strongly pushing the rupee in one direction, intervention can only do so much. Plus, excessive intervention can deplete the country’s foreign exchange reserves, which isn’t a sustainable strategy in the long run. A common mistake I see people make is thinking of this as a simple fix. It’s a complex balancing act, requiring careful judgment and coordination with other economic policies.
Moreover, the effectiveness of intervention depends on credibility. If the market believes the RBI is committed to defending the rupee, intervention is more likely to succeed. But if the market senses hesitation or uncertainty, intervention might be less effective, and could even backfire. The Central Bank also considers the impact of global crude oil prices on inflation to plan intervention.
Also, the emergence of global economic uncertainty adds a layer of complexity. Factors like rising US interest rates, geopolitical tensions, and fluctuations in foreign portfolio investment can all impact the rupee. So, the RBI has to consider all these moving parts when deciding whether and how to intervene.
The Big Picture | What’s Next for the Rupee?
So, what’s the takeaway here? Rupee intervention is a complex tool used by the RBI to manage the currency and maintain economic stability. It affects everyone, from exporters and importers to the average person on the street. While it’s not a perfect solution, it plays a crucial role in navigating the ever-changing landscape of the Indian economy.
Looking ahead, the future of the rupee will depend on a variety of factors, including global economic conditions, domestic policies, and the RBI’s actions. Keeping a close eye on these developments is essential for anyone with a stake in India’s economic future. One thing you absolutely must double-check is to avoid relying solely on predictions – the markets are fickle, so understanding the underlying dynamics is key. Also, consider how bitcoin plunge might impact broader market confidence.
FAQ
Why does the RBI intervene in the rupee’s value?
The RBI intervenes to manage volatility, control inflation, and maintain economic stability. A rapidly depreciating or appreciating rupee can have negative consequences for the Indian economy.
How does the RBI intervene in the currency market?
The RBI primarily intervenes by buying or selling foreign currency reserves, usually US dollars, in exchange for rupees. This alters the supply and demand for rupees, influencing its value.
What are the risks of rupee intervention?
Excessive intervention can deplete foreign exchange reserves and may not be effective if global factors are strongly pushing the rupee in one direction.
Who benefits from rupee intervention?
A stable rupee benefits most stakeholders by keeping inflation in check and maintaining investor confidence. Exporters may benefit from a weaker rupee, while importers prefer a stronger rupee.
How often does the RBI intervene?
The RBI intervenes as needed, depending on market conditions and the overall economic outlook. There’s no set schedule; it’s a dynamic decision.
What if the RBI doesn’t intervene?
Without intervention, the rupee could become excessively volatile, leading to increased inflation, reduced investor confidence, and potential economic instability. So, it’s a crucial tool, even if it’s not always a perfect solution.




